 |
 |
 |
 | Generalized nonhyperbolic moveout approximation |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Connection with other approximations
Up: Fomel & Stovas: Generalized
Previous: INTRODUCTION
Let  represent the reflection traveltime as a function of the
source-receiver offset
represent the reflection traveltime as a function of the
source-receiver offset 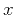 . We propose the following general form of
the moveout approximation:
. We propose the following general form of
the moveout approximation:
 |
(1) |
The five parameters  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  describe the moveout behavior. By simple algebraic manipulations, one
can also rewrite equation 1 as
describe the moveout behavior. By simple algebraic manipulations, one
can also rewrite equation 1 as
 |
(2) |
where the new set of parameters  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  is
related to the previous set by the equalities
is
related to the previous set by the equalities
The inverse transform is given by
The existence of the nonhyperbolic part in the traveltime
approximation 1 and 2 is controlled by parameter
 . When
. When  is zero (which implies that
is zero (which implies that  or
or  ),
approximation 1 is hyperbolic. When both
),
approximation 1 is hyperbolic. When both  and
and  are
very large, approximation 2 also reduces to the hyperbolic
form.
are
very large, approximation 2 also reduces to the hyperbolic
form.
Subsections
 |
 |
 |
 | Generalized nonhyperbolic moveout approximation |  |
![[pdf]](icons/pdf.png) |
Next: Connection with other approximations
Up: Fomel & Stovas: Generalized
Previous: INTRODUCTION
2013-03-02
![]() represent the reflection traveltime as a function of the
source-receiver offset
represent the reflection traveltime as a function of the
source-receiver offset ![]() . We propose the following general form of
the moveout approximation:
. We propose the following general form of
the moveout approximation: