Contributing new programs to Madagascar: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
→Static code checks: links |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
If you want to share your code with other Madagascar users: | If you want to share your code with other Madagascar users: | ||
# Follow the guide on [[Adding new programs to Madagascar]]. | # Follow the guide on [[Adding new programs to Madagascar]]. | ||
# If your employer holds the copyright for your software, obtain | # If your employer holds the copyright for your software, obtain permission to distribute under a [http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.html GPL license] and place a copyright and GPL license notice in each file with code. | ||
# [https://github.com/ Sign up at GitHub]. | # [https://github.com/ Sign up at GitHub]. | ||
# Upload your directory to the [https://github.com/ahay/src Github repository] by making a pull request. | # Upload your directory to the [https://github.com/ahay/src Github repository] by making a pull request. | ||
# Announce your changes in the release notes for the upcoming stable version ([https://github.com/ahay/src/blob/master/NEWS.txt $RSFSRC/NEWS.txt]) | # Announce your changes in the release notes for the upcoming stable version ([https://github.com/ahay/src/blob/master/NEWS.txt $RSFSRC/NEWS.txt]) | ||
# Make sure to add reproducible examples of using your program under the <tt>$RSFSRC/book</tt> tree. Create new directories if necessary and commit them to the repository. As a rule, programs without examples | # Make sure to add reproducible examples of using your program under the <tt>$RSFSRC/book</tt> tree. Create new directories if necessary and commit them to the repository. As a rule, the release version does not include programs without examples. | ||
Some additional | Some additional helpful information is included below. | ||
==Repository procedure suggestions== | ==Repository procedure suggestions== | ||
For coding style suggestions, please see [[Adding_new_programs_to_Madagascar#Style_guide | the "Adding new programs" section]]. | Please try to do [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_commit atomic commits]. For coding style suggestions, please see [[Adding_new_programs_to_Madagascar#Style_guide | the "Adding new programs" section]]. | ||
==Backward compatibility features== | ==Backward compatibility features== | ||
If you introduce or notice a feature that is used solely for | If you introduce or notice a feature that is used solely for backward compatibility with an old version of a dependency, please document it here so that the feature can be eliminated when the Madagascar community stops supporting that version of that dependency<ref>This could be more elegantly done by using a special string to flag a backward compatibility comment in the code, then have the documentation builder build this list automatically. This would make it more likely for this page to be kept in sync with the codebase.</ref>. | ||
==Mitigating missing dependencies== | ==Mitigating missing dependencies== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 20: | ||
==Reasons for the existence of certain features== | ==Reasons for the existence of certain features== | ||
===Why pyc files are generated during the install step=== | ===Why pyc files are generated during the install step=== | ||
Python bytecode files, with the pyc extensions, are created during the <tt>scons install</tt> | Python bytecode files, with the pyc extensions, are created during the <tt>scons install</tt> to: | ||
* Register them in SCons' dependency tree | * Register them in SCons' dependency tree so that <tt> scons remove them -c install</tt> | ||
* Avoid a situation | * Avoid a situation where a user tries to execute a Madagascar Python program but creates the pyc file during a module import fails because of lack of write access to <tt>$RSFROOT/lib</tt>. | ||
==cfortran.h== | ==cfortran.h== | ||
This source code file provides a machine-independent interface between C procedures, Fortran procedures and global data (more details [http://www-zeus.desy.de/~burow/cfortran/ on the website of its initial author]). It is a dependency of the F77 and F90 APIs, as well as of vplot. It is included in m8r in <tt>api/f90</tt> with a link in <tt>api/f77</tt>. Version 4.3 (2002) is still distributed through | This source code file provides a machine-independent interface between C procedures, Fortran procedures, and global data (more details [http://www-zeus.desy.de/~burow/cfortran/ on the website of its initial author]). It is a dependency of the F77 and F90 APIs, as well as of vplot. It is included in m8r in <tt>api/f90</tt> with a link in <tt>api/f77</tt>. Version 4.3 (2002) is still distributed through the original author's website. Another version (fork?) is [http://root.cern.ch/viewvc/trunk/montecarlo/eg/inc/cfortran.h?view=log maintained at CERN] and distributed in the include directory of the interface to event generators in the Monte Carlo libraries in the [http://cernlib.web.cern.ch/cernlib/ CERN Program Library] (CERNlib). Debian distributes the Free Software part of this package as <tt>cernlib</tt>. Under Fedora, <tt>cfortran.h</tt> is included in <tt>cernlib-g77-devel</tt> and <tt>cernlib-devel</tt>, which happily overwrite each other's files and create copies of <tt>cfortran.h</tt> in two different locations deeply nested under <tt>/usr/include</tt>. CERNlib's Debian maintainer states that [http://people.debian.org/~kmccarty/cernlib/index.html "CERNlib is an ancient mass of mostly Fortran code"] and that [http://people.debian.org/~kmccarty/physics-software-rant.html "Most components of CERNLIB are completely broken on modern 64-bit architectures"], so m8r developers should be aware that CERNlib will probably be superseded in the future by [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ROOT ROOT], with upstream <tt>cfortran.h</tt> maintenance possibly continuing this way. | ||
==Static code checks== | ==Static code checks== | ||
Madagascar contains the beginning of an implementation of static code checks for security vulnerabilities and coding mistakes with [http://www.splint.org/ Splint]. This is visible in the code through the presence of comments like <tt>/*@out@*/</tt> and <tt>/*@null@*/</tt>, which instruct Splint about the intent of different variables and function return values. | Madagascar contains the beginning of an implementation of static code checks for security vulnerabilities and coding mistakes with [http://www.splint.org/ Splint]. This is visible in the code through the presence of comments like <tt>/*@out@*/</tt> and <tt>/*@null@*/</tt>, which instruct Splint about the intent of different variables and function return values. Plans include dynamic checking by [http://valgrind.org/ Valgrind] or IBM's [http://www-306.ibm.com/software/awdtools/purify/ Rational Purify]. Madagascar code metrics are [https://openhub.net/p/m8r assessed periodically by Open Hub]. | ||
==Maintaining the maintenance tools== | ==Maintaining the maintenance tools== | ||
Please document scripts | Please document scripts that maintain the Madagascar codebase and save them in <tt>$RSFSRC/admin</tt>. Cleanup procedures may need to be repeated in the future, as authors are human and can make the same mistakes again. | ||
==Information flow map== | ==Information flow map== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 38: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
==Dual licensing Madagascar code== | ==Dual licensing Madagascar code== | ||
In a contractual work relationship, you may find it handy to reuse some of your existing public code for which you own the copyright. This may also apply if you are doing contract work for a client on behalf of your employer, who owns the copyright. | |||
If your code does not have any GPL-ed dependencies, and the copyright owner agrees to | If your code does not have any GPL-ed dependencies, and the copyright owner agrees to release the code under a different license than the GPL, then you are free to go ahead and do it. However, make sure that in every file you state the following: | ||
* who is the copyright owner, | * who is the copyright owner, | ||
* what are the terms of the proprietary license that it is being released under, | * what are the terms of the proprietary license that it is being released under, | ||
* that the code has already been licensed to the public under the GNU GPL | * that the code has already been licensed to the public under the GNU GPL before this as part of the Madagascar package | ||
It is important to specify all these items, lest years later, someone in your client's company finds the code, realizes that similar code is part of Madagascar, and wrongly believes that the copyright belonged to his company | It is important to specify all these items, lest years later, someone in your client's company finds the code, realizes that similar code is part of Madagascar, and wrongly believes that the copyright belonged to his company and that you infringed it by releasing the code under the GPL. | ||
Ensure that proper copyright and licensing statements are in place in case of dual licensing, even if you are on excellent terms with your client and are confident they will not falsely accuse you of wrongdoing. Companies get acquired, employees and even owners leave companies, policies and business strategies change, and old contracts, licenses, and legal documents get discarded or lost in a mass of old junk. Each source code file should contain all the relevant copyright and licensing information. | |||
Latest revision as of 03:32, 26 November 2024
If you want to share your code with other Madagascar users:
- Follow the guide on Adding new programs to Madagascar.
- If your employer holds the copyright for your software, obtain permission to distribute under a GPL license and place a copyright and GPL license notice in each file with code.
- Sign up at GitHub.
- Upload your directory to the Github repository by making a pull request.
- Announce your changes in the release notes for the upcoming stable version ($RSFSRC/NEWS.txt)
- Make sure to add reproducible examples of using your program under the $RSFSRC/book tree. Create new directories if necessary and commit them to the repository. As a rule, the release version does not include programs without examples.
Some additional helpful information is included below.
Repository procedure suggestions[edit]
Please try to do atomic commits. For coding style suggestions, please see the "Adding new programs" section.
Backward compatibility features[edit]
If you introduce or notice a feature that is used solely for backward compatibility with an old version of a dependency, please document it here so that the feature can be eliminated when the Madagascar community stops supporting that version of that dependency[1].
Mitigating missing dependencies[edit]
The main idea is to attempt to provide graceful degradation when facing a missing dependency. Quoting the Wikipedia page on fault-tolerant systems, this "enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of (or one or more faults within) some of its components. If its operating quality decreases at all, the decrease is proportional to the severity of the failure, as compared to a naively-designed system in which even a small failure can cause total breakdown."
Reasons for the existence of certain features[edit]
Why pyc files are generated during the install step[edit]
Python bytecode files, with the pyc extensions, are created during the scons install to:
- Register them in SCons' dependency tree so that scons remove them -c install
- Avoid a situation where a user tries to execute a Madagascar Python program but creates the pyc file during a module import fails because of lack of write access to $RSFROOT/lib.
cfortran.h[edit]
This source code file provides a machine-independent interface between C procedures, Fortran procedures, and global data (more details on the website of its initial author). It is a dependency of the F77 and F90 APIs, as well as of vplot. It is included in m8r in api/f90 with a link in api/f77. Version 4.3 (2002) is still distributed through the original author's website. Another version (fork?) is maintained at CERN and distributed in the include directory of the interface to event generators in the Monte Carlo libraries in the CERN Program Library (CERNlib). Debian distributes the Free Software part of this package as cernlib. Under Fedora, cfortran.h is included in cernlib-g77-devel and cernlib-devel, which happily overwrite each other's files and create copies of cfortran.h in two different locations deeply nested under /usr/include. CERNlib's Debian maintainer states that "CERNlib is an ancient mass of mostly Fortran code" and that "Most components of CERNLIB are completely broken on modern 64-bit architectures", so m8r developers should be aware that CERNlib will probably be superseded in the future by ROOT, with upstream cfortran.h maintenance possibly continuing this way.
Static code checks[edit]
Madagascar contains the beginning of an implementation of static code checks for security vulnerabilities and coding mistakes with Splint. This is visible in the code through the presence of comments like /*@out@*/ and /*@null@*/, which instruct Splint about the intent of different variables and function return values. Plans include dynamic checking by Valgrind or IBM's Rational Purify. Madagascar code metrics are assessed periodically by Open Hub.
Maintaining the maintenance tools[edit]
Please document scripts that maintain the Madagascar codebase and save them in $RSFSRC/admin. Cleanup procedures may need to be repeated in the future, as authors are human and can make the same mistakes again.
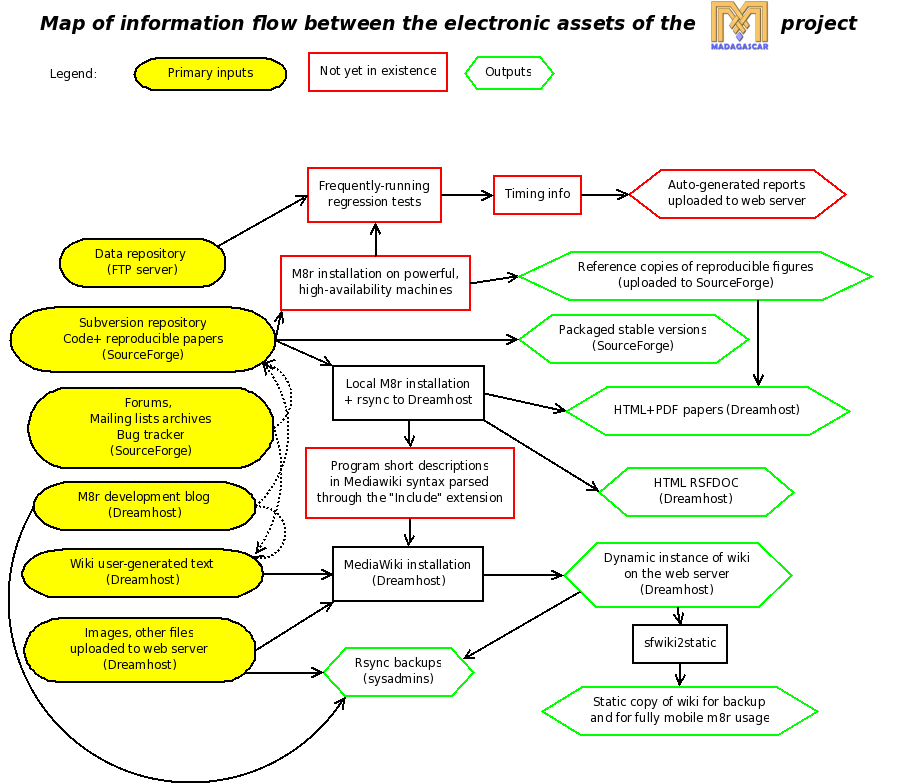
Information flow map[edit]
The vector graphics original of this map in Dia format is available upon request through the rsf-devel mailing list.
- ↑ This could be more elegantly done by using a special string to flag a backward compatibility comment in the code, then have the documentation builder build this list automatically. This would make it more likely for this page to be kept in sync with the codebase.
Dual licensing Madagascar code[edit]
In a contractual work relationship, you may find it handy to reuse some of your existing public code for which you own the copyright. This may also apply if you are doing contract work for a client on behalf of your employer, who owns the copyright.
If your code does not have any GPL-ed dependencies, and the copyright owner agrees to release the code under a different license than the GPL, then you are free to go ahead and do it. However, make sure that in every file you state the following:
- who is the copyright owner,
- what are the terms of the proprietary license that it is being released under,
- that the code has already been licensed to the public under the GNU GPL before this as part of the Madagascar package
It is important to specify all these items, lest years later, someone in your client's company finds the code, realizes that similar code is part of Madagascar, and wrongly believes that the copyright belonged to his company and that you infringed it by releasing the code under the GPL.
Ensure that proper copyright and licensing statements are in place in case of dual licensing, even if you are on excellent terms with your client and are confident they will not falsely accuse you of wrongdoing. Companies get acquired, employees and even owners leave companies, policies and business strategies change, and old contracts, licenses, and legal documents get discarded or lost in a mass of old junk. Each source code file should contain all the relevant copyright and licensing information.