A new paper is added to the collection of reproducible documents: Automatic channel detection using deep learning
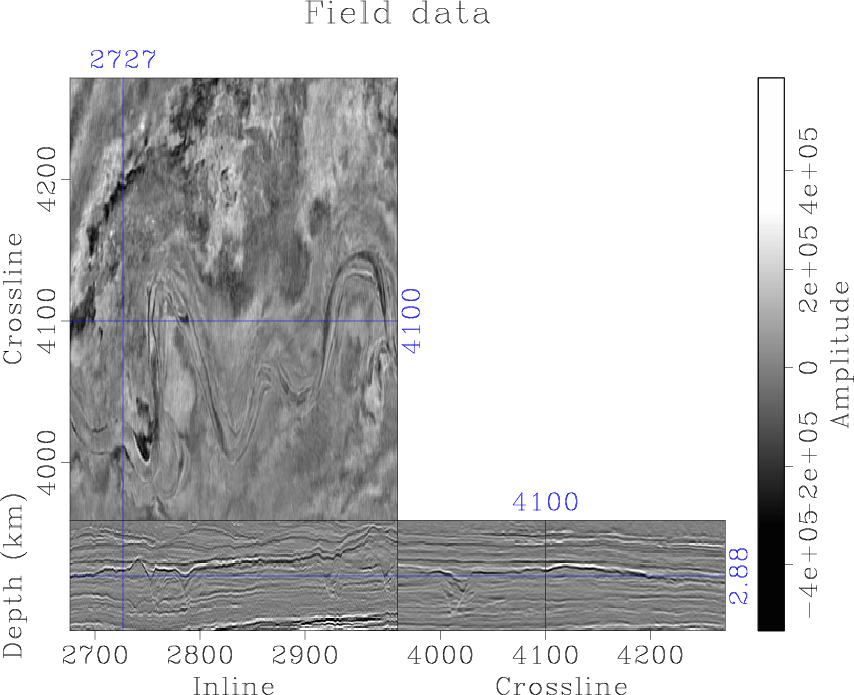
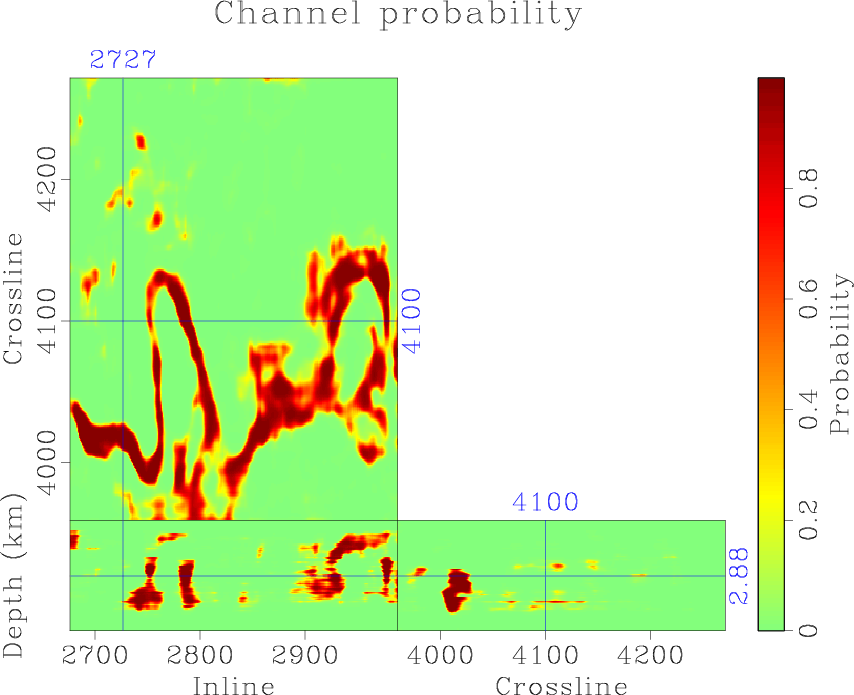
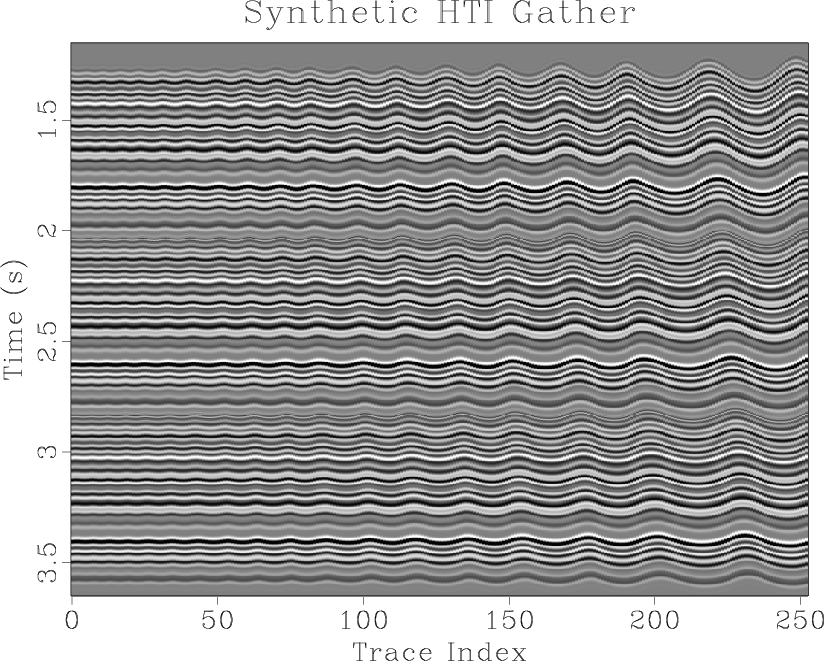
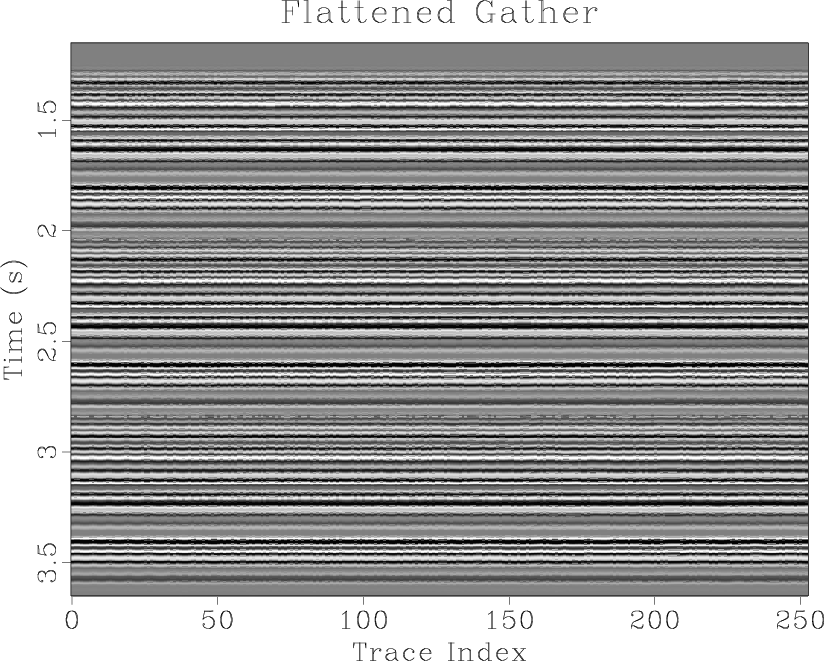
We propose a method based on an encoder-decoder convolutional neural network for automatic channel detection in 3D seismic volumes. We use two architectures borrowed from computer vision which are SegNet for image segmentation together with Bayesian SegNet for uncertainty measurement. We train the network on 3D synthetic volumes and then apply it to field data. We test the proposed approach on a 3D field dataset from the Browse Basin, offshore Australia and a 3D Parihaka seismic data in New Zealand. Applying the weights estimated from training on 3D synthetic volumes to a 3D field dataset accurately identifies channel geobodies without the need for any human interpretation on seismic attributes. Our proposed method also produces uncertainty volumes to quantify the trustiness of detection model.